Aims and Functions of the OECD
The aims of the OECD are clearly stated in the OECD Convention. It aims to promote policies to make the world richer, freer, fairer, and more stable, not only for members but also for non-member countries. Simply put, promoting better policies for better lives is what the OECD is aiming for.

OECD members believe a stronger, cleaner, and fairer world is possible through co-operation, sharing information and ideas, and mutual advice. What does the OECD do to achieve this? The organisation is proud of its evidence-based research and analysis. Therefore, OECD discussions are based on objective data, and decisions are made by consensus, in principle, among the members after discussion.
Decisions are implemented and monitored by peer reviews and multilateral surveillance. How do peer reviews work? Simply, experts from other countries closely examine one country's policies or practices in a specific area. These experts look for ways the country being examined can improve its policies, but they also look for lessons and good practices that can benefit others.
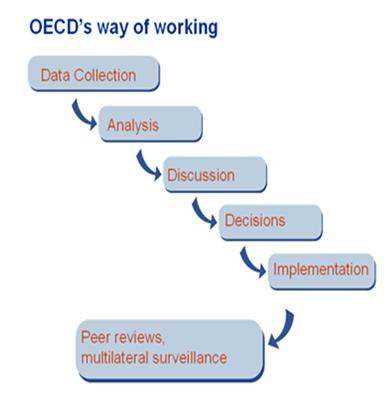
In fact, the peer-review process has often been referred to as “international group therapy,” where countries can openly discuss their problems and look to peers for objective guidance, advice, and support of the OECD.
The OECD applies peer pressure through another method, commonly referred to as soft law. Soft law is a formal international promise among countries to aspire to higher standards. It has no legally binding components but is a very effective tool for positive change through peer pressure. Countries often pass national legislation based on the principles that they have agreed to aspire to and uphold on an international level. This approach has the advantage of allowing each country to adapt agreements to its own national legislative and governing environment. One of the best examples of both peer review and soft law is the OECD/G20 BEPS projects on international tax practices, which involves bringing about tax transparency in secretive jurisdictions and addressing corporate profit shifting.
Although the OECD stands for Economic and Development, its scope is not limited to these elements. Its work spans a variety of policy areas. One might say the OECD produces advice and global standards on almost everything, such as improving education standards, enacting fair international tax systems, providing affordable health care, fighting corruption and bribery, and even monitoring tractors.

source : OECD, https://www.oecd.org/about/how-we-work/

